Friends,
When the Dimension table and the Fact Table(also called as Measure Group Table) are related through some other dimension table then that type of relationship is called as Referenced Relationship Type. Lets take a small example from AdventureWorks database.
I am taking the following tables to demonstrate Referenced relationship type.
1) FactInternetSales – Fact/Measure group table
2) DimProduct and DimProductSubCategory – Dimension tables
In this case FactInternetSales and DimProduct tables have foreign key relationship on the column “ProductKey” and hence to fetch Product wise sales then the query looks like –
Select EnglishProductName,sum(sales_Amount) from FactInternetSales
INNER JOIN DimProduct on FactInternetSales.ProductKey = DimProduct.ProductKey
Group by EnglishProductName
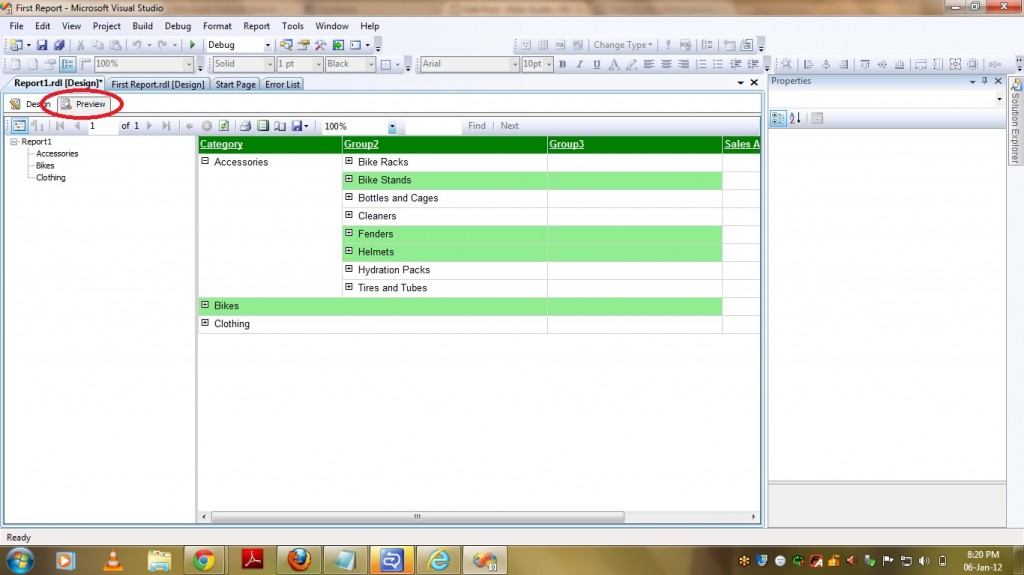
Now if you wish to get data at Subcategory Level then the query looks like –
Select EnglishProductSubcategoryName,sum(sales_Amount) from FactInternetSales
INNER JOIN DimProduct on FactInternetSales.ProductKey = DimProduct.ProductKey
INNER JOIN DimProductSubcategory on DimProductSubcategory.ProductSubcategoryKey = DimProduct.ProductSubcategoryKey
Group by EnglishProductSubcategoryName
If you observe the above query then it is clear that We are not using any column to display from DIMPRODUCT table but still we are using it to give reference between DimProductSubcategory table and FactInternetSales tables.
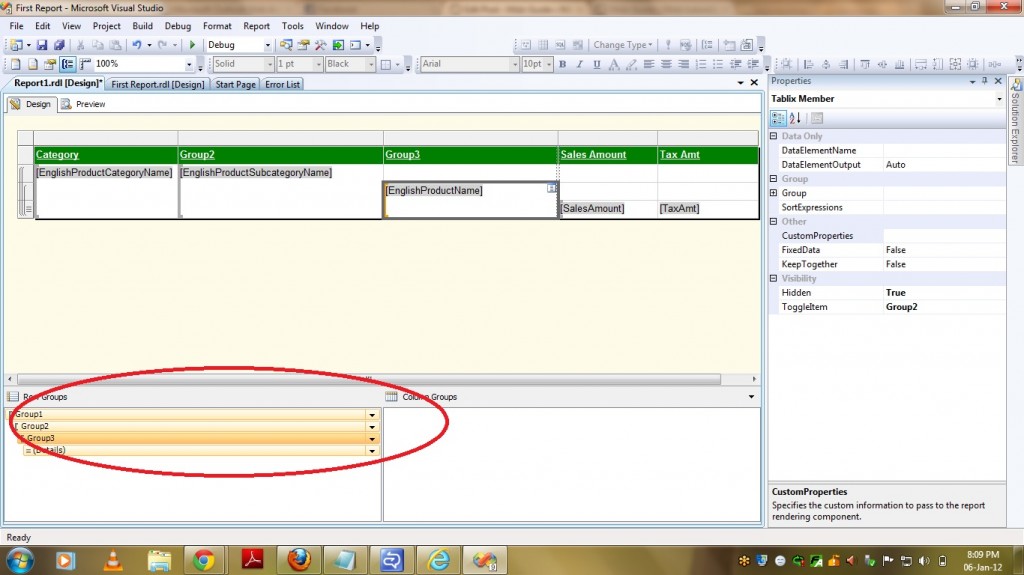
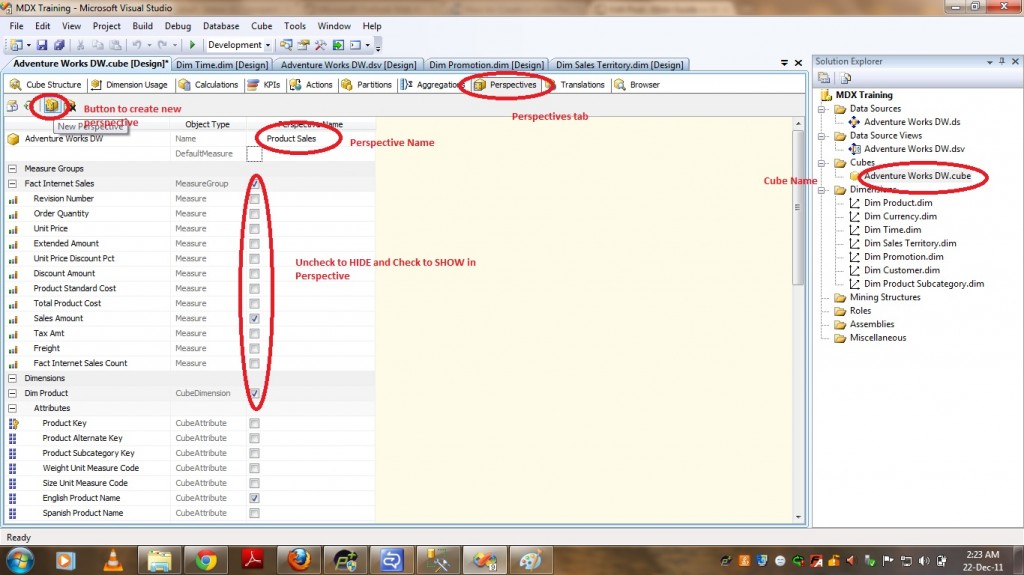
We used INNER JOIN to join FactInternetSales and DimProduct tables and the same relationship can be provided in SSAS cube which is called as Regular Relationship Type. As we cannot give regular relationship type between FactInternetSales and DimProductSubcategory tables as they dont have KEY to join(in other words not directly related), we can use REFERENCED Relationship type to relate those two tables. If we want to relate the above query with SSAS Cube implementation then DimProduct and DimProductSubcategory tables are Dimension Tables in Cube and FactInternetSales is Fact Table . PFB the screen with out providing relationship between dimension and fact.
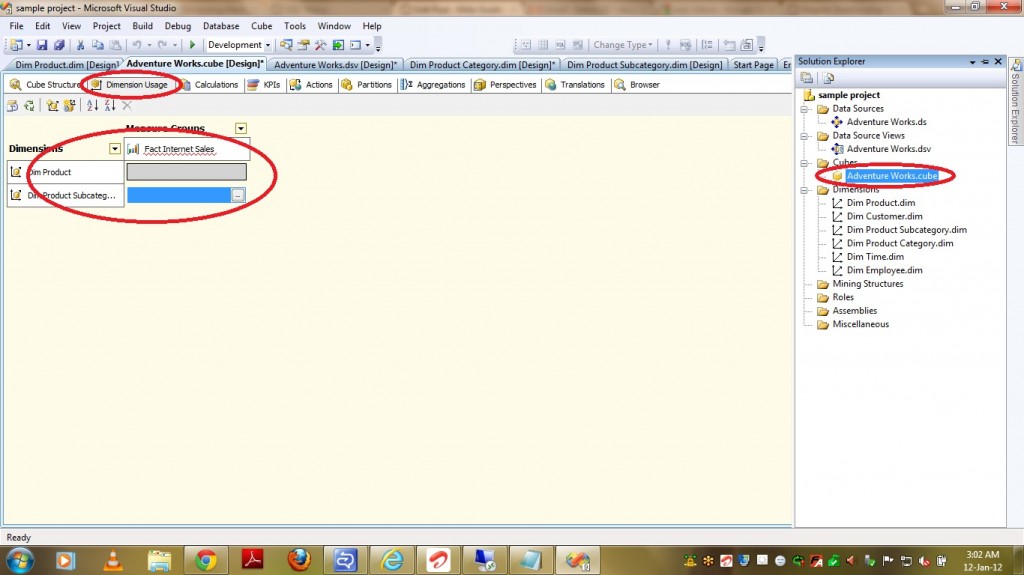
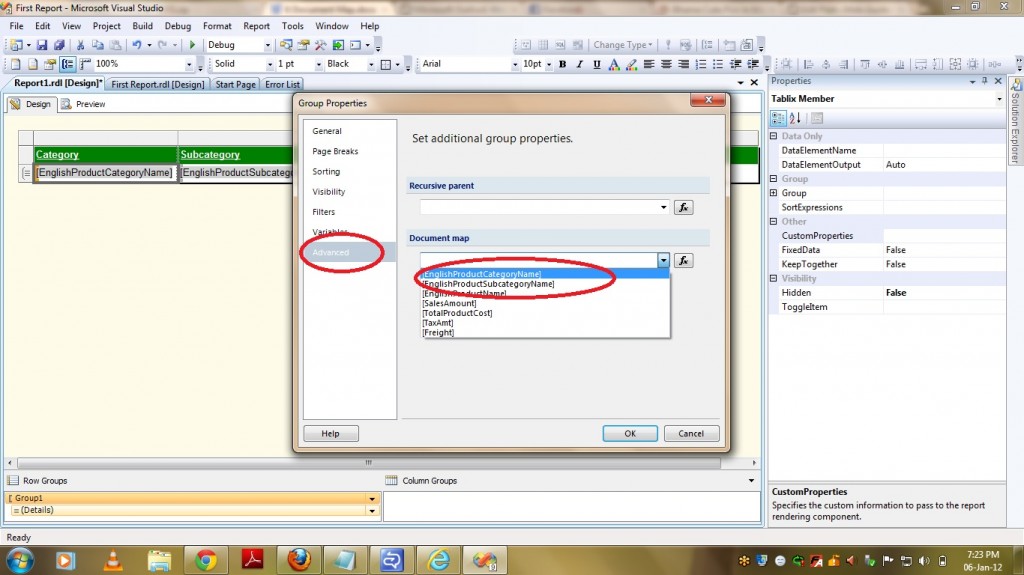
Now lets see the steps to be followed to provide Regular Relationship Type between a dimension(DimProduct) and a Measure Group(FactInternetSales). Use the Define Relationship dialog box to define a relationship between a cube dimension and a measure group in Cube Designer. You can display the Define Relationshipdialog box by clicking … on a cell in the Grid pane on the Dimension Usage tab in Cube Designer.
2) Select the attribute that defines the granularity of the measure group with respect to the dimension. This attribute is usually the key attribute of the dimension.(ProductKey in our case).
3) Then it automatically displays Dimension Table and Fact Table.
4) It also displays the Dimension Table columns in RELATIONSHIP GRID and you have to select appropriate Measure Group Columns.
PFB the screenshot of the same.
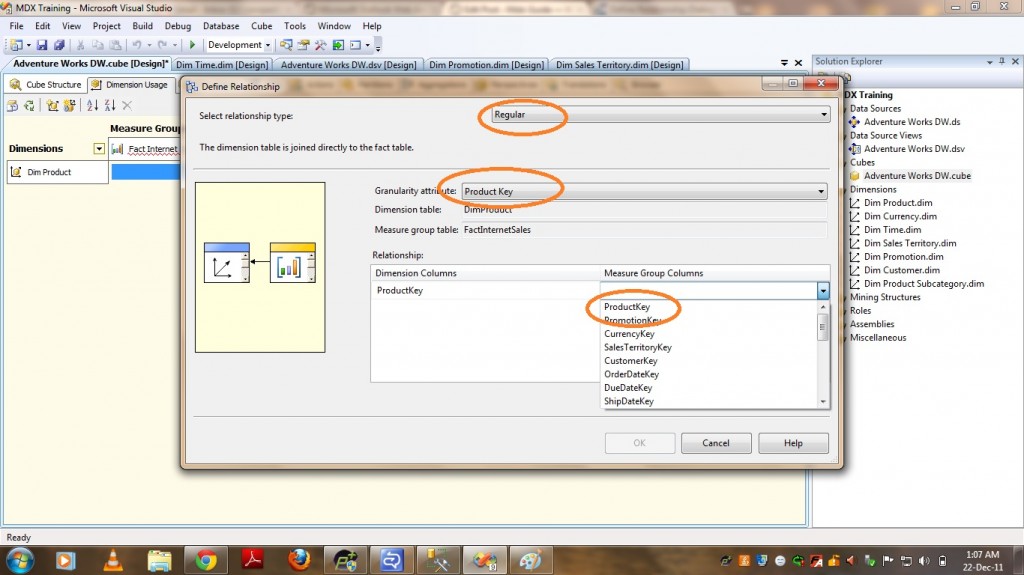
5) After selecting Measure Group Columns click OK.
We set the relationship between InternetSales and Product using Regular relationship type. Now lets see how to give referenced relationship between FactInternetSales and DimProductSubCategory. Before going to that following things should be in mind while giving referenced relationship type.
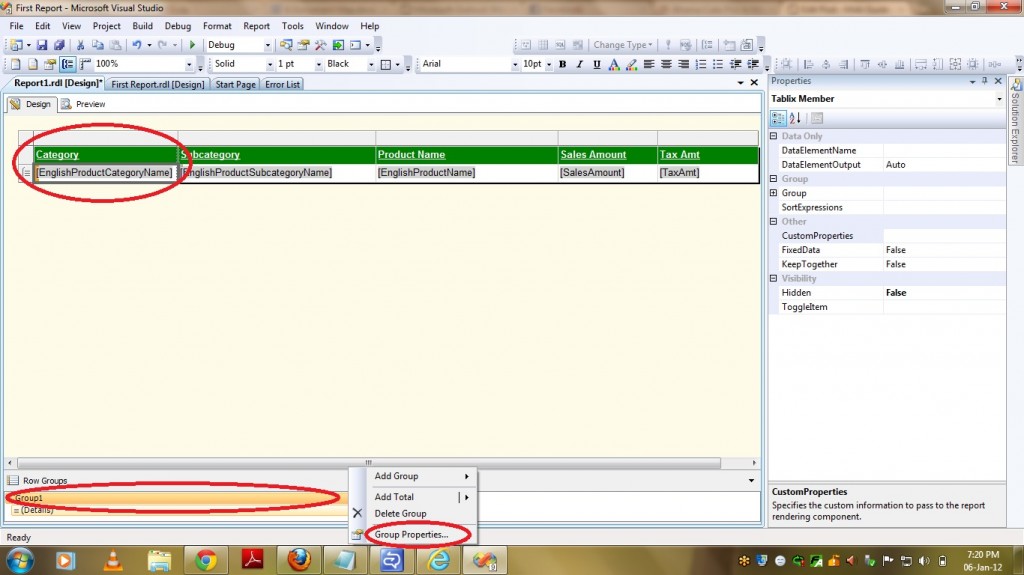
1) The dimension which is acting as Intermediate should be created first.
2) The columns that are required to join the fact and second dimension should be selected as Attributes in the Intermediate dimension. From the above SQL query it is clear that my DimProduct dimension(which acts as bridge between fact and subcategory) requires a min of two columns as attributes and i.e ProductKey to join with Fact and ProductSubcategoryKey to join with DimProductSubcategory Dimension.
Now please find the steps below to give referenced relationship –
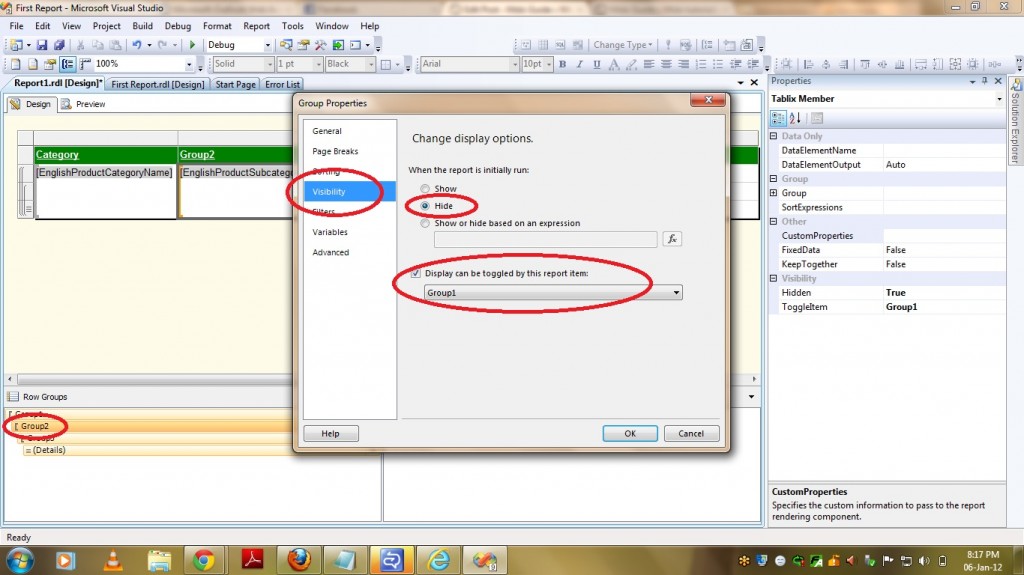
1) Select the relationship Type as “Referenced”.
2) Select the intermediate Dimension(In our case it is Dim Product).
3) Select the attributes from both the dimensions which forms a relationship between these two dimensions(In our case it is ProductSubCategoryKey).
4) Materialize option is checked and leave it as it is.
5) Click on OK.
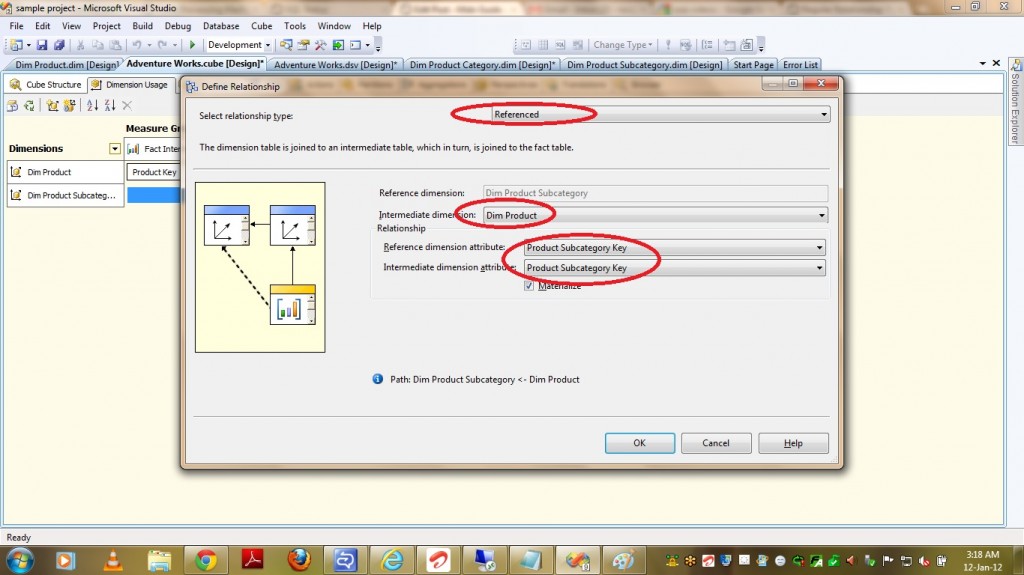
That’s it .. It is as easy as this .. Happy Coding !!
Regards,
Roopesh Babu V